The structures that give blood its color and carry oxygen are called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the substance that forms the main structure of red blood cells (red blood cells). The lifespan of red blood cells in the body is about 120 days. After 120 days, the red blood cells in the blood are destroyed and renewed. When this hemoglobin substance in red blood cells is broken down, it is converted into bilirubin. Bilirubin is a yellow-colored substance. The liver is responsible for removing bilirubin from the body. However, if bilirubin cannot be removed from the body sufficiently for any reason, it enters the blood circulation and causes the skin, mucous membranes and eye whites to appear yellow.
Jaundice
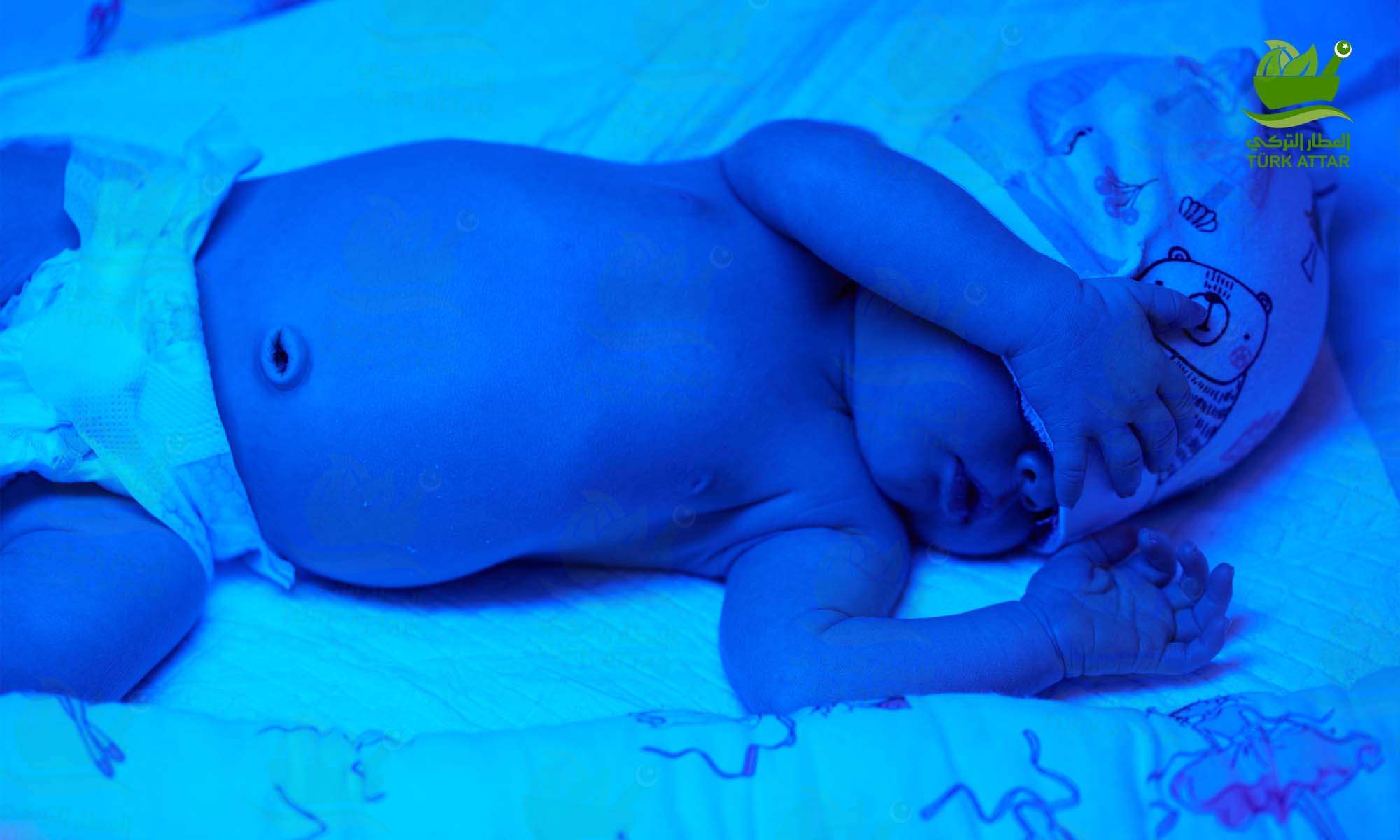
What is jaundice in babies?
Jaundice observed in infants is called neonatal jaundice. It is possible to encounter jaundice in many new-borns. Jaundice can be observed in 80% of premature babies and 80% of babies born after 37 weeks. Jaundice in babies can have many causes. One of the most common causes is physiological jaundice. Babies' livers have just taken over the task of breaking down bilirubin after birth from the placenta. The developing liver is not able to remove bilirubin effectively at first, as time passes, the liver removes bilirubin effectively and the symptoms disappear on their own.
What are the symptoms of jaundice in babies?
Neonatal jaundice may present with symptoms such as increased sleepiness, change in stool and urine color, and difficulty in sucking in infants. Jaundice begins in the head and spreads throughout the body. In increasing jaundice, organs such as hands and feet turn yellow. If a late-onset type of jaundice is observed in infants, it is usually due to breast milk jaundice. This type of jaundice can last for about 2-3 months. As long as the bilirubin level in the blood does not reach the dangerous limit, breast milk is not interrupted. If high bilirubin is not treated, it can cause permanent brain damage.
What are the symptoms of jaundice?
Symptoms of jaundice in older children and adults can be listed as follows;
Jaundice in the eyes and skin
Itching
Weakness/fatigue
darkened urine
light colored stool
Stomach ache
weight loss
Fever.
What is jaundice?
Although jaundice is actually a medical condition that occurs for different reasons, hepatitis B disease is also called jaundice among the people. Caused by the hepatitis B virus, hepatitis B is a disease that can be transmitted through blood or sexually, causing damage to the liver and causing serious consequences such as liver cancer if left untreated. This virus is carried in some people for years without showing any symptoms. Carriers can transmit the disease to others without realizing it.
What are the types of jaundice?
Because jaundice can occur for different reasons, it has been classified into three broad categories based on causal factors. The classification is based on which part of the liver is malfunctioning and how the excretion of bilirubin from the bloodstream is affected. Types of jaundice according to their causes; It is classified as hepatocellular, hemolytic and obstructive jaundice.
Hepatocellular Jaundice: Hepatocellular jaundice is a type of jaundice that occurs due to damage to the liver. Damage can occur for a variety of reasons. If the parenchymal cells in the liver are affected for reasons such as infection, a decrease in liver metabolism is observed. As a result of decreased metabolism, bilirubin cannot be removed from the body and begins to accumulate. The jaundice disease caused by hepatitis A, B or C viruses is actually classified as hepatocellular jaundice. Liver cancer or excessive alcohol consumption can also cause liver damage.
Hemolytic Jaundice: Hemolytic jaundice occurs when red blood cells in the bloodstream break down faster than normal. In such a situation, the liver cannot cope with the high level of bilirubin. This condition, known as hemolysis, can be fatal. Hemolytic jaundice is found in patients with malaria. Malaria parasites rapidly attack red blood cells, causing them to break down.
Obstructive Jaundice: Obstructive jaundice is a type of jaundice that results from obstructions between the bile ducts that connect the liver, gallbladder and intestine. This blockage prevents the liver from removing bilirubin, and the increased bilirubin in the liver negatively affects liver metabolism. Obstructive jaundice can occur due to many diseases that can cause a blockage in the bile ducts. Gallstones or swollen lymph nodes can cause blockages in this duct.
How is jaundice diagnosed?
Jaundice is detected by measuring the amount of bilirubin in the blood or urine. Bilirubin levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Adults and older children should have blood bilirubin levels between 0.3 and 0.6 mg/dL. About 97 percent of babies born after 37 weeks have bilirubin levels less than 13 mg/dL. Patients with levels higher than this are referred to the relevant units for further investigation.
