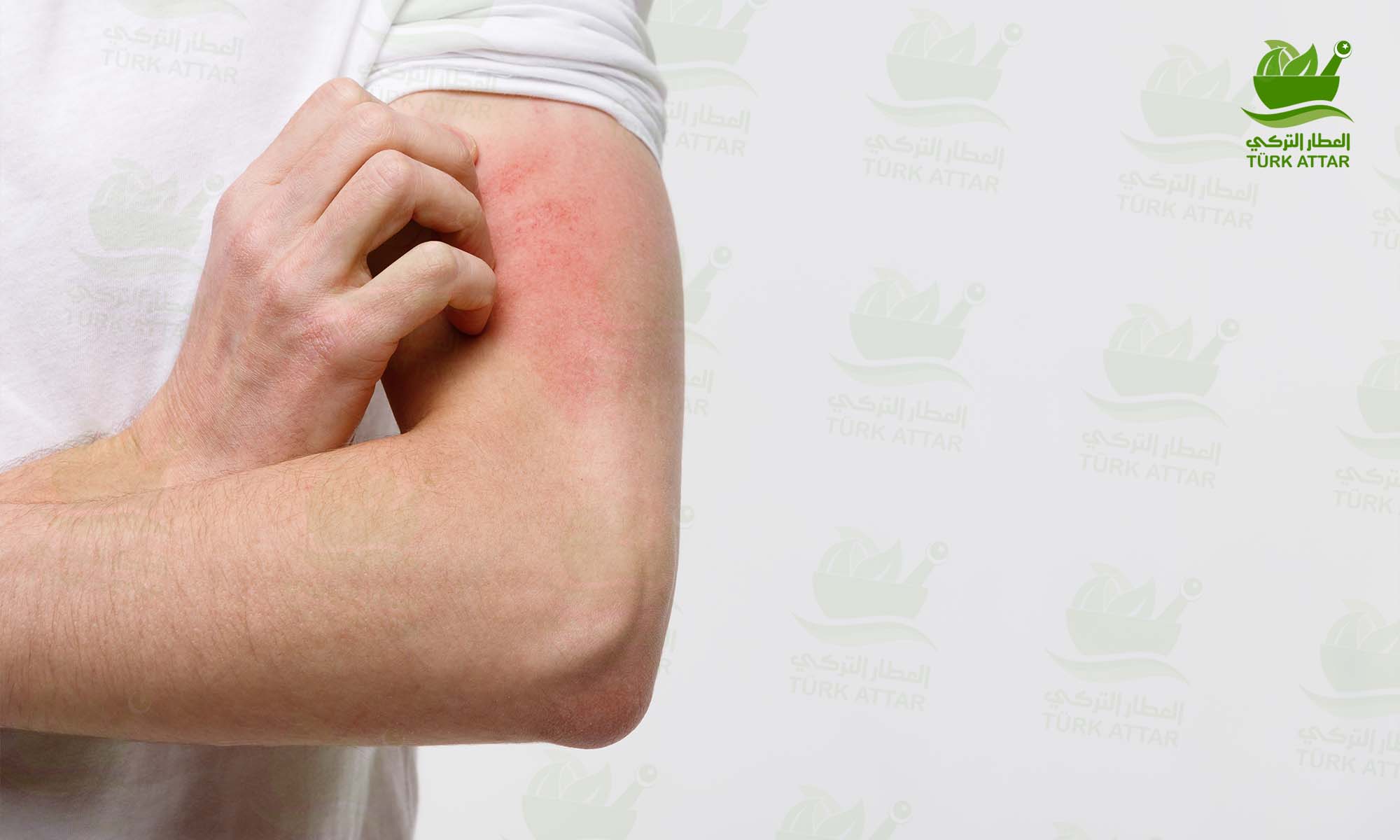
Urticaria rash and accompanying blisters are caused by the release of histamine and other chemicals into the bloodstream by certain cells.
What is Hives?
Hives, popularly known as urticaria, is a skin disease characterized by raised, itchy and reddened patches caused by skin reactions due to different conditions.
These red spots can vary in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres, and they can commonly merge with each other and cover a very large area on the skin. The spots may appear and disappear within 24 hours during the course of the disease.
Urticaria are not contagious.
If the rash and blisters from urticaria persist for more than six weeks and recur frequently over months or years, the condition is considered chronic urticaria. People with chronic urticaria can be very bothersome. It can interfere with sleep or daily activities. Antihistamines and anti-itch medications to be taken with the advice of a doctor can lead to relief in individuals suffering from the condition.
Reasons
What Causes Hives or urticaria?
urticaria rash and accompanying blisters are caused by the release of histamine and other chemicals into the bloodstream by certain cells.
Medical professionals often cannot identify the cause of chronic urticaria or why acute urticaria sometimes becomes chronic. However, it is known that some of the triggering causes of rash on the skin are as follows:
pain relievers
Alcohol use
Insects or parasites
Various types of food
Prolonged pressure on the skin, like a rubber band
scratching
Exercise
Infection
Sunlight
Cold
Stress
high temperature
However, in some cases, chronic urticaria may be associated with another underlying medical condition such as thyroid disease or, rarely, cancer.
Symptoms
What Are the Symptoms of Hives?
The most common of the signs and symptoms of chronic hives are red or skin-colored patches that can appear anywhere on the body. In addition, swellings that change in size, appear and disappear during the day, and very hard itching are another symptom.
Painful swelling of the lips, eyelids, and throat, angioedema, may also occur. It has been observed that the symptoms of hives intensify during fatigue, stress, heat and exercise. Chronic urticaria may continue uninterruptedly for more than six weeks and recur over the years, but short-term, acute urticaria, appears suddenly and disappears within a few weeks.
If blisters and redness are seen that continue to appear for several days, it is absolutely necessary to consult a skin specialist, namely a dermatologist. Chronic urticaria by itself does not put the individual at risk of a serious allergic reaction, anaphylaxis.
However, emergency care may be required if the individual is showing signs of hives, among other symptoms, as part of a severe allergic reaction. Signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis include dizziness, shortness of breath, and swelling of the lips, eyelids, and tongue.
Diagnostic Methods
How Is Hives Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of hives is usually made after a physical examination by a dermatologist. The specialist will ask the patient a series of questions to understand why the signs and symptoms are causing them.
However, in order to monitor the situation, the individual may be asked to keep a daily list of daily activities, medications, herbal remedies or supplements taken, eating and drinking during the diet, in which area the hives appear and how long they last, or whether the hives are accompanied by painful swellings.
As a result of the physical examination and medical history, if the doctor concludes that the hives are caused by a separate underlying medical problem, they may request a series of blood tests and skin tests.
